Hints for Your clinical stepwise approach for examining the eye lidswith particular regard to ptosis)
Shake hands to exclude for myotonia (note slow release of grip)
Observe
• Face for asymmetry
• Brow for overactive forntalis
• Globes for position and asymmetry
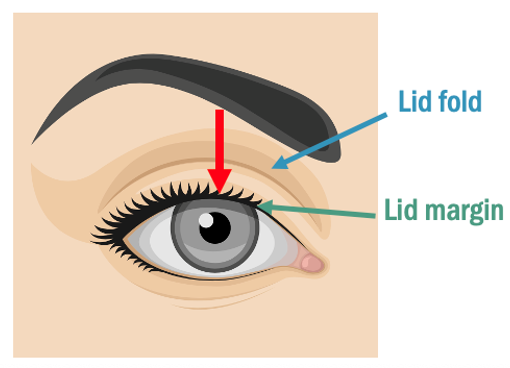
• Lids for position,asymmetry or scars
• Pupils anisocoria or heterochromia.
Measure palpebral aperture
Measure upper margin reflex distance
Measure position of upper lid crease
Measure levator function
• Inhibit frontalis by placing a thumb on the brow
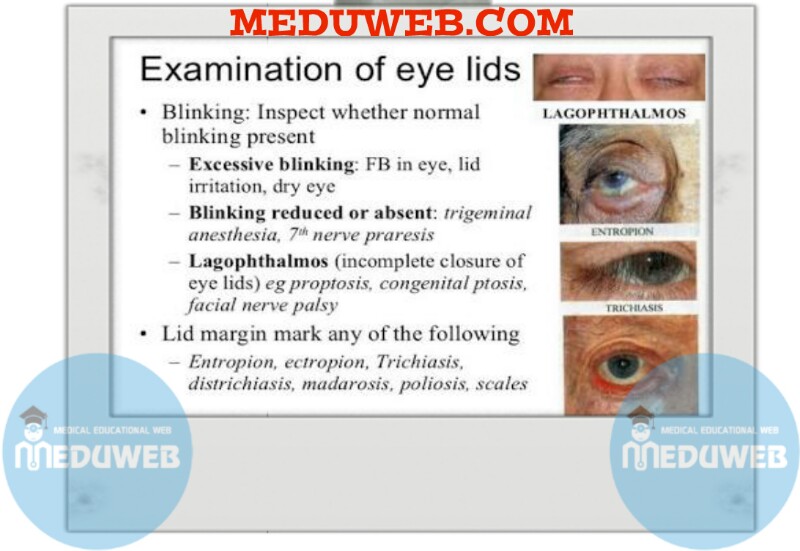
Measure any lagophthalmos
• Ask patient to close eyes, gently at first, and then to squeeze eyes shut
Assess orbicularis function and Bell’s phenomenon
• Try to open patient’s eyes against resistance
Assess fatiguability over 1 min for worsening of ptosis
• Ask patient to keep looking upward at a target held superiorly
Examine for Cogan’s twitch Any overshoot of ptosis
• Ask patient to look rapidly from downgaze to a target held in 1ry position
Assess for jaw-winking For any change in ptosis
• Ask patient to simulate chewing and to move jaw from side to side
Slitlamp examination of lid and subtarsal conjunctiva for Inflammation,masses or scars
Check corneal sensation very Prognostic for any lid surgery
Examine ocular motility
• motility abnormality
• change in ptosis
Examine pupils
• Anisocoria (in response to light and near)
• iris heterochromia
Consider: ice-pack test for MG
Full cranial n. assessment
• ( 2nd , 3rd ,4th ,5th ,6th and 7th )
Examination of fundus
Systemic review (myopathy, fatiguability)
Normal lid measurements gift of ptosis
Palpebral aperture 8–11 mm (♀ > ♂)
Upper margin reflex distance 4–5 mm
Upper lid excursion (levator function) 13–16 mm
Upper lid crease position 8-10 mm from margin (♀ > ♂)
Examining the eye lids hints power point presentations:
THE EYELID Dr. Samten Dorji PG Resident Ophthalmology ( Examining the eye lids hints )
Eye Lid ( Examining the eye lids hints )
Ptosis ( Examining the eye lids hints )
- Functional anatomy • Levator palpebrae superioris (LPS): – is the primary muscle responsible for lid elevation. – It arises from the back of the orbit and extends forwards over the cone of eye muscles. – It inserts into the eyelid and the tarsal plate, a fibrous semicircular structure which gives the upper eyelid its shape. – The LPS is supplied by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve. • Muller’s muscles: – The way that the LPS attaches to the tarsal plate is modified by the underlying Müller’s muscle. – This involuntary muscle, comprising sympathetically innervated smooth muscle, – has the capacity to ‘tighten’ the attachment and so raise the lid a few millimetres. ( Examining the eye lids hints )
- • Frontalis & orbicularis oculi: – frontalis muscle and the orbicularis oculi, both supplied by the facial nerve. – Frontalis contraction helps to elevate the lid by acting indirectly on the surrounding soft tissues, – while orbicularis oculi contraction depresses the eyelid. ( Examining the eye lids hints )
- DEFINITION • Ptosis (from Greek Ptosis -to “fall”) is a drooping or falling of the upper or lower eyelid. ( Examining the eye lids hints )
- CLASSIFICATION OF PTOSIS A. Congenital B. Acquired 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Neurogenic Myogenic Aponeurotic Mechanical Neurotoxic C. Pseudotosis ( Examining the eye lids hints )
Examining the eye lids hints Videos:
Disorders of the Eye Lid – CRASH! Medical Review Series – YouTube ( Examining the eye lids hints )
Examination of the Eyes and Vision – OSCE Guide ( Examining the eye lids hints )
Examining the eye lids hints