Medical treatment in pediatric glaucomas
Although management of pediatric glaucomas is almost always surgical( due to abnormal angle development),,, medical ttt has also a big role with special precautions ( whenever surgery is contraindicated or has to be postponed for awhile).
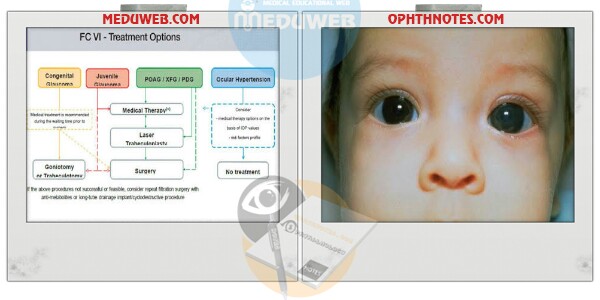
So there are some critical points have to considered in Medical treatment in pediatric glaucomas:
• 1st line drug is topical beta blockers ( lowest dose, gel form once daily ) serious side effects should be monitored ( apnea, bronchospasm,heart block)
•2nd line drug topical CAI
•3rd line systemic CAI with high precautions ( metabolic acidosis, renal failure, aplastic anemia)
NB in Medical treatment in pediatric glaucomas:
•PG has no role in pediatric glaucomas specially below age of 8 due to abnormal uveoscleral pathway( not well developed or abnormally developed)
•pilocarpine has no role due to trabeculodysgenesis and drug intolerance (induced myopia)
• alpha agonist absolutely contraindicated below 2 yrs of age better to be avoided as much as possible due to CNS complications and if necessary the patient weight should be over 20 kg
We have to know that children below 8 years are extremely steroid responder more than adults with marked IOP rise within 15 days ( as steroids not only block trabecular meshwork with deposited GAG ( glycosaminoglycans) particles but also alter the normal trabecular development as it is immature till the age of 8 yrs )
Medical treatment in pediatric glaucomas PowerPoint presentation :
Congenital and pediatric glaucoma
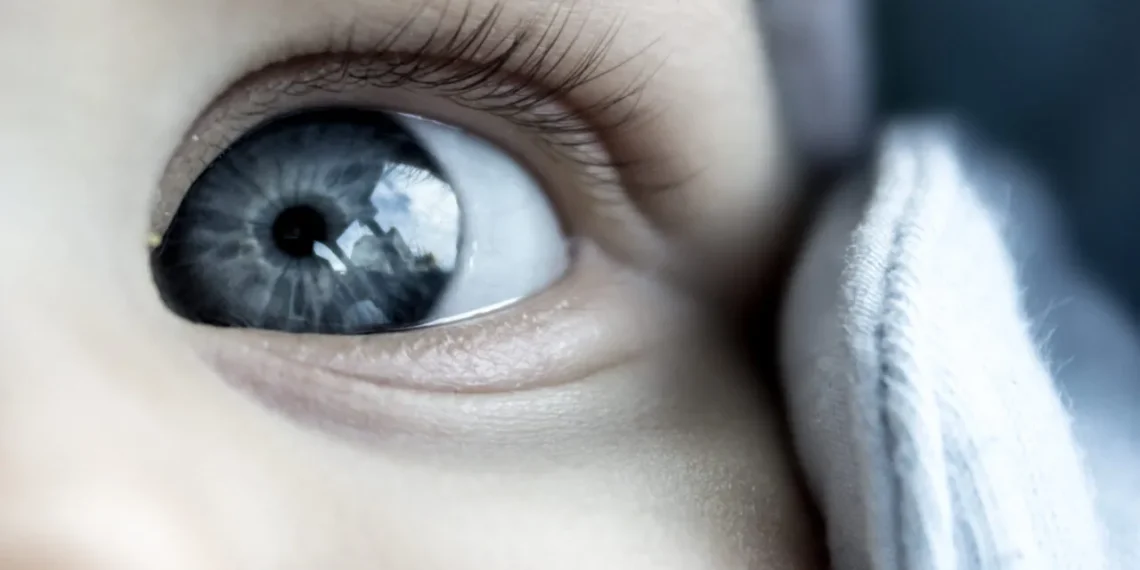
They are a group of diverse disorders in which abnormal high intraocular pressure results due to developmental abnormalities of the angle of anterior chamber obstructing the drainage of aqueous humour.
Congenital and pediatric glaucoma case presentation Presenter- Dr. Ajinkya Kulkarni Moderator- Dr. Rita Dhamankar
Definition Relating to age of onset Congenital glaucoma: The glaucoma exists at birth, and usually before birth. Infantile glaucoma: Occurs from birth until 3 years of life. Juvenile glaucoma: Occurs after the age of 3 to teenage years. Developmental glaucoma: Glaucoma associated with developmental anomalies of the eye present at birth. Primary developmental glaucoma: Resulting from maldevelopment of the aqueous outflow system. Secondary developmental glaucoma: Resulting from damage to the aqueous outflow system due to maldevelopment of some other portion of the eye, e.g., angle closure due to pupillary block in a small eye, or an eye with microspherophakia or dislocated lens; or as a forward shift of the lens-iris diaphragm in persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous or retinopathy of prematurity.