Optical coherence tomography ( OCT)
✍️ high-resolution images of the neurosensory retina in a non-invasive manner.
✍️ analogous to ultrasonography but measures light waves, rather than sound waves.
✍️ OCT measurements are achieved indirectly using interferometry.
✍️ the combination of light reflected from a tissue of interest and light reflected from a reference path produces characteristic interference patterns
✍️ interference pattern dependent on the mismatch between the reflected waves.
✍️ Since the time delay and amplitude of one of the waves (the reference path) are known, the time delay and intensity of light returning from the sample tissue may be determined.
✍️ The resulting plot of light intensity versus time delay is known as an A-scan and describes the anatomy of the eye tissue at a specific point.
✍️ A-scans are then repeated at multiple transverse locations and mapped to a grey or false-colour scale, giving rise to two-dimensional cross-sectional (tomographic) images (termed B-scans).
✅ Indications about Optical coherence tomography
✍️ Monitoring of response to treatment and/or disease activity in patients with chorioretinal vascular and inflammatory diseases (neovascular AMD, diabetic retinopathy, RVO, CMO).
✍️ Diagnosis of clinically occult macular pathology (subtle abnormalities of the vitreoretinal interface).
✍️ Detection of glaucomatous damage to the RNFL and/or optic nerve head.
✍️ Assessment and longitudinal monitoring of disc volume in disc swelling and papilloedema.
✅Interpretation in Optical coherence tomography
✍️ On OCT false-colour B-scans, highly reflective tissue is reddish white in colour, while hyporeflective tissue is blue–black in colour.
✍️ Alternatively, images can be shown in 256 shades of grey, corresponding to different optical reflectivities
✍️ The inner and outer nuclear layers and ganglion cell layer are typically hyporeflective
✍️ the inner and outer plexiform layers and nerve bre layer are hyperreflective.
✍️ larger retinal vessels are seen on OCT as circular hyperreflective foci located in the inner retina, with underlying ‘shadowing’
✍️ A number of hyperreflective bands may be seen in the outer retina, typically consisting of
• the external limiting membrane
• photoreceptor inner segment-outer segment (IS-OS) junction (ellipsoid zone)
• RPE.
✍️ Using specialized scanning protocols (enhanced depth imaging) the choroid and choroidal–scleral junction may also be seen.
✅ Technology in Optical coherence tomography
✍️ Time domain OCT ( TD/OCT) using the Stratus OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec) acquires images at 400 axial scans/s, with an axial resolution of 10 microns.
✍️ Spectral (or Fourier) domain (SD/OCT) using the Spectralis HRA/OCT (heidelberg Engineering) or Cirrus HD-OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec) scan at a rate of at least 20,000 axial scans/s, with an axial resolution typically between 3 and 8 microns.
✅ Quantitative image analysis in Optical coherence tomography
✍️ measure retinal thickness at multiple locations and to construct retinal thickness maps corresponding to the ETDRS subfields.
✍️ automated quantitative assessment of drusen and geographic atrophy in patients with AMD.
✍️ In patients with glaucoma
• specialized circular OCT scanning protocols are employed
• a single circular B-scan, centred on the optic disc and 3.4mm in diameter, is obtained.
• Segmentation of the inner and outer boundaries of the RNFL allows assessment of peripapillary RNFL thickness.
• The presence of glaucomatous RNFL thinning can then be determined by comparison with normative databases.
✅ how to comment on Optical coherence tomography
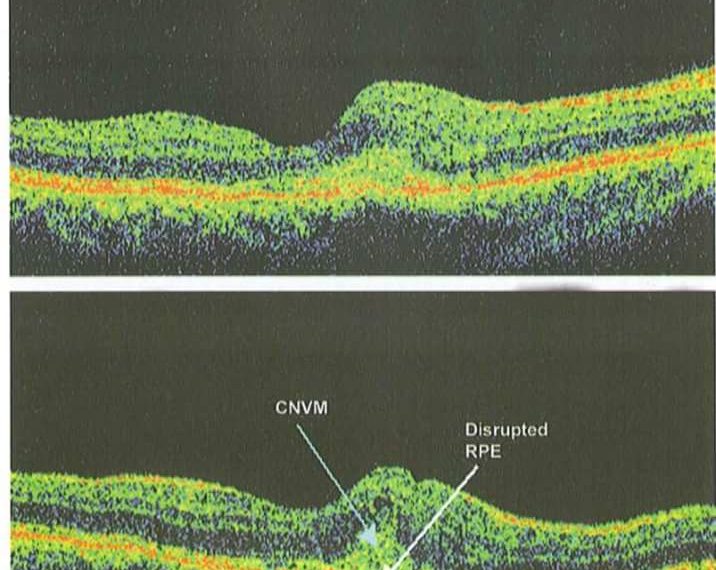
As follows
I can see the following
✍️ increased retinal foveal thickness
✍️ disruptions of RPE layer
✍️ infront of the RPE , there is mild hyperreflective mass with smaller hyporeflective lacunae or spaces
✍️ all other layers are will differentiated with increased thickness and hyporeflective minute intervening spaces ( oedema)
✅ Conclusion:
✍️ Classic CNV picture of OCT
Optical coherence tomography powerpoint presentations :
Optical Coherence Tomography
OCT is a non contact, non invasive, micron resolution cross-sectional study of retina which correlates very well with the retinal histology.
It was unbelievable, histopathology without biopsy of a structure which was literally untouchable (Retina).
Optical coherence tomography Videos:
(What is OCT Scanning? (Optical Coherence Tomography
https://m.youtube.com/watch?t=8s&v=BxRAAVr7oA8