Retinoscopy hints
ROOM LIGHTS OFF
Ask patient to look at a non-accommodative target distance (green duochrome).
Compensate your working distance ( if you work at 2/3m, add +1.50 D DS).
Fog fellow eye with a high plus powered lens to prevent accommodation.
Aim to be as close to the patient’s visual axis without obscuring their fixation target.
If your head gets in the way, they are likely to look at it and start accommodating.
Ask the patient to tell you if this happens.
Check retinoscopy reflex
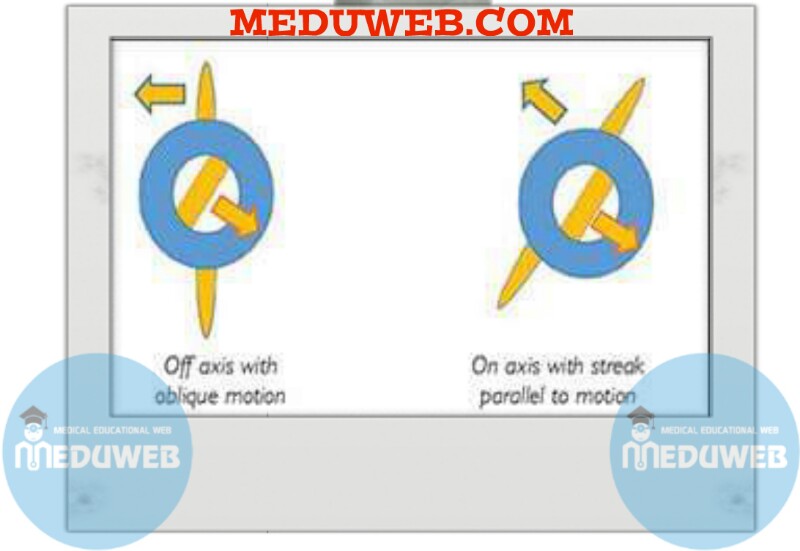
Identify axis of astigmatism from movement of retinoscopy light as sweep across eye.
Neutralize reflex in one meridian with DS lenses.
If reflex is (with) then add PLUS, if (against) then add MINUS.
When point of reversal is reached in one meridian add cylindrical lenses to neutralize in the other meridian.
Use Plus or minus cylinders and Be consistent either work with plus or with minus cylindrical lenses.
If using PLUS cylindrical lenses, correct the most MINUS meridian .
This is identified by
If both reflexes are against, then it is the slower reflex.
If one is with and one against, then it is the against reflex.
If both reflexes are with, then it is the faster reflex.
If using MINUS cylindrical lenses, correct the most PLUS meridian.
This is identified similarly
If both reflexes are against, then it is the faster reflex.
If one is with and one against, then it is the with reflex.
If both reflexes are with, then it is the slower reflex.
Poor reflex
Consider media opacity
optimize illumination
check patient not accommodating on your head.
Consider high refractive error
use large steps, e.g. ± 5.00 DS or ±10.00 DS.
Consider keratoconus
if swirling or scissoring reflex or oil drop sign.
A retinoscope objectively determine the spherocylindrical refractive error and irregular astigmatism, and also evaluate opacities and irregularities of the cornea and lens.
Most retinoscope today use a streak projection system. This streak of light is reflected from a mirror.
the streak can be moved in relation to a convex lens in the device by way of the sleeve. This allows the light to leave the device as if it were coming from a point behind the retinoscope ( plano mirror setting) which routinely used , or as if it were coming from a point between the examiner and the patient (concave mirror setting).
For Copeland retinoscopes, the plano position is with the sleeve up, while the Welch Allyn retinoscope is in the plano position with the sleeve down.
Normally, the examiner will use their right eye to perform retinoscopy on the patient’s right eye and their left eye for the patient’s left eye.
The examiner should align themselves just off-center to minimize lens reflections and to allow the patient to visualize the distance target to relax their accommodation.
The patient should be instructed( from time to time ) to look at a distance target such as a large Snellen letter (20/200-20/400).
When doing retinoscopy, the examiner is attempting to put the far point of the patient’s eye at the plane of the examiner’s pupil.
When the reflex shows “against” motion, the far point plane lies between the patient’s eye and the examiner’s eye, indicating myopia.
When the reflex shows “with” motion, the far point lies outside the interval between (the patient’s eye and the observer’s eye), indicating hyperopia, emmetropia or mild myopia.
let’s make a Question to be simply understood
If you obtain “with motion” during retinoscopy,
Where is the far point of the patient ???
• in front of the peep hole
• at the peep hole
• beyond the peep hole?
Answer: Beyond the peephole. As u r dealing with hypermetrope
The goal of neutralization is to have the light reflex of the patient’s far point at the peephole.
The light at the patient’s pupil fills the entire space at once when neutrality is reached.
“With” motion requires more plus to be added to the prescription to move the far point to neutralization.
“Against” motion means that the far point is in front of the peephole. Therefore, more minus must be added to move the far point to neutralization.
Retinoscopy PowerPoint presentations:
Retinoscopy and its principles
Retinoscopy by Dr. D.Y.Patil Optometry College
Retinoscopy hints Videos:
Ophthalmology – Retinoscopy (Part 1/2)
Ophthalmology – Retinoscopy (Part 2/2) – YouTube
Retinoscopy hints