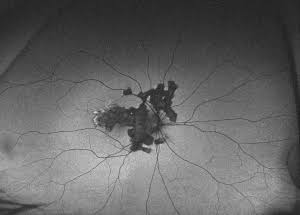
Serpiginous Choroidopathy
• Rare, usually bilateral
• mostly affecting Caucasians of either sex.
• Also called geographic choroidopathy.
• typically as a middle-aged adult with active choroidal inflammation adjacent to previous scars.
• May present at a younger age (>10 years) .
• slow stepwise progression with spread from the peripapillary area towards the periphery.
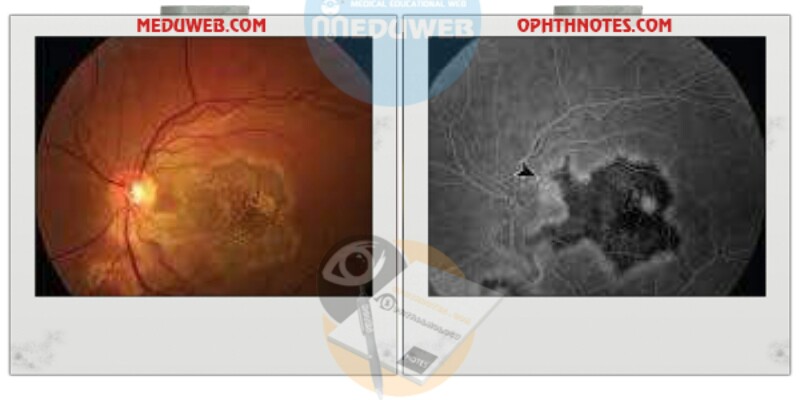
Active lesions show early blockage with late staining on FFA .
• Often treated with systemic steroids for vision-threatening lesions, although not of proven benefit.
• Extrafoveal CNV is treated with argon laser with steroid umbrella.
Serpiginous Choroidopathy power point presentations:
Choroiditis
1. Dr. Samarth Mishra CHOROIDITIS
2. INTRODUCTION • Inflammation of choroid; associated with the highest risk of severe vision loss. (Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group) • Always Involving retina, Retinal vessels, optic nerve head.
3. CLASSIFICATION ANATOMICAL – Choroiditis Chorioretinitis Retinochoroiditis Neuro-uveitis AETIOLOGICAL – infective/non-infective
4. INFECTIOUS 1. Parasitic – Toxoplasmosis – Toxocariasis – Onchocerciasis – Cysticercosis 2. Bacterial – – tuberculosis – syphilis 3. Viral – Herpes viruses • ARN • CMV retinitis Epstein-Barr virus – Rubella – Rubeola (measles) – West Nile virus
5. 3. Fungal – Candidiasis – Aspergillosis – Cryptococcosis – Coccidioidomycosis
6. NON-INFECTIOUS CAUSE Multifocal Choroiditis and Panuveitis Punctate Inner Choroidopathy Subretinal Fibrosis and Uveitis Serpiginous choroidopathy Acute retinal pigment epitheliitis Birdshot choroidopathy Retinal Vasculitis – Behcets – SLE – Wegeners granulomatosis – PAN – Eales disease – Frosted-branch angiitis
7. SYMPTOMS Floaters Impaired central vision ( pain or painless ) Pain, redness & photophobia if associated with ant. Segment involvement Metamorphopsia, micro/macropsia Perception of black spot
8. SIGNS – Inflammatory cells & vitritis Exudates, Edema & infiltrations in retina / choroid Sheathing of vessels Other signs – Disc edema Retinal haemorrhages Spill-over uveitis Complicated cataract Glaucoma RD Choroid neovascularisation
9. CHOROIDITIS Focal / multifocal /diffuse/central/ juxtapapillary Granulomatous or non-granulomatous/ exudative choroiditis Ophthalmoscopic picture – 1 . Active lesion – early stage – yellowish area with hazy edges & ill defined margin due to infiltration & exudation , lie deeper to retinal vessels – Late stage – bruch’s membrane destroyed – infiltration of leukocytes to retina & vitreous ↓ organisation of exudation due to fibroblastic activity of stroma ↓ Firm fusion of retina & choroid due to destruction of normal structure by fibrous tissue
10. Old choroiditis lesion – – White colour lesion due to fibrous tissue deposition, thinning & atrophy – white reflex from sclera Surrounded by black zone of pigment from RPE RETINITIS – Focal /multifocal / geographic /diffuse Active lesions – whitis retinal opacities with indistinct boarder due to surronding edema Later on boarder become well defined VASCULITIS – Periphlebitis > periarteritis Active vasculitis – yellowish/grey-white, patchy perivascular sheathing, with hemorrhage.
Serpiginous Choroidopathy